Seed Funding Program 2022
SETDB1i
SETDB1 SMOL inhibition as an enhancer of anti-cancer immunity
Coordinators
 dkfz.de
dkfz.de
Jochen Utikal
Dermatological Clinic, UMM

Nikolas Gunkel
Cancer Drug Development, DKFZ
Detailed description
SETDB1 is a lysine methyl transferase, which regulates cancer hallmarks like proliferation, migration and immune evasion. Recent papers and own unpublished observations have shown that loss of SETDB1 enhances the intrinsic immunogenicity of cancer cells via the mobilization of endogenous retro elements, resulting in a pronounced interferon-ß response, increased antigen presentation and thereby enhancement of the efficacy of cancer immune therapies. This new role of SETDB1 is currently derived only from genetic “loss of function” experiments. The project aims to identify the first SMOL
inhibitor for SETDB1, which will allow moving its validation status beyond what can be achieved with genetical manipulations and correlation analysis. An assay cascade will be used to demonstrate that chemical inhibition alters cellular drug effect markers like histone methylation, expression of dsRNA encoded by retro elements, interferon ß response as well as quantification of the antigen presenting machinery.
This data package will be the basis for a future Hit to lead/Lead optimization process and a preclinical Proof of Concept for immune checkpoint inhibition.
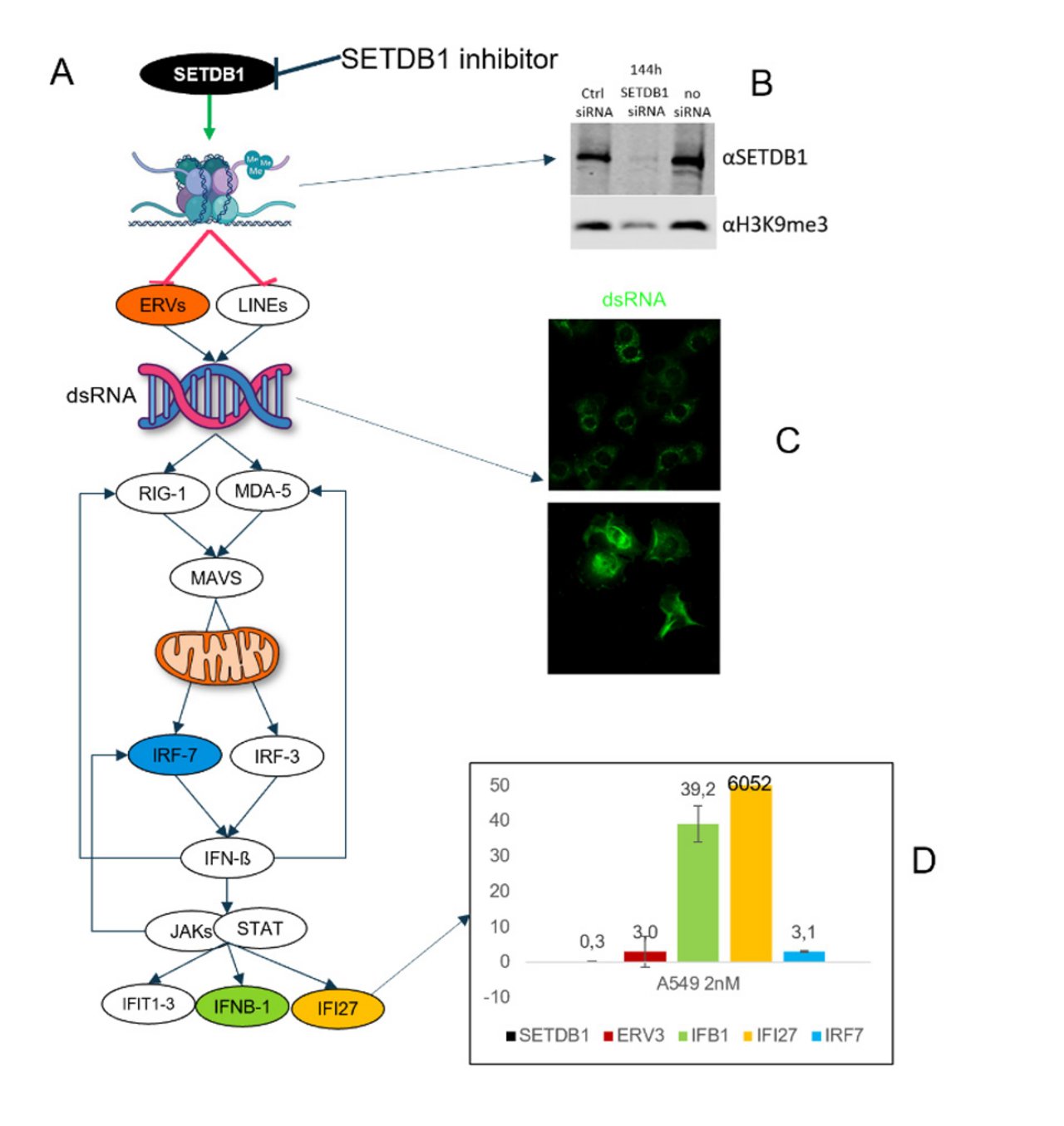
A: SETDB1 is a histone methyle transferase which sticks methyl on defined residues of histone H3 and thereby regulates the expression of ancient retroviruses (ERV) and other retro elements (LINEs). When SETDB1 is expressed at high levels, ERVs are repressed. When SETDB1 is inhibited, ERVs are becomming active and express double stranded RNA (dsRNA, typical for retroviruses). dsRNA is recognized by a set of proteins (RIG-1, MDA-5 and MAVS) which signal the cell that retroviruses are active and that the cell needs to take care of this problem. It does so by inducing interferon response genes (IRFs and IFIs) which mediate the apropriate response.
B: Genetic reduction of SETDB1 expression leads to a reduction of methylated histone 3, visualized by western blot.
C: This results in an increase of dsRNA in cells, visualized by in situ staining.
D: The cell reacts to dsRNA by upregulating the anti-viral response genes IFB1, IFI27 and IRF7.